Deep Dive: Solana Onchain Activity - June 2025
Deep Dive: Solana Onchain Activity - June 2025




Note: Below is the text-accessible version of this post for visually impaired readers.
Syndica Deep Dive: Solana Onchain Activity - June 2025
Part I - Network
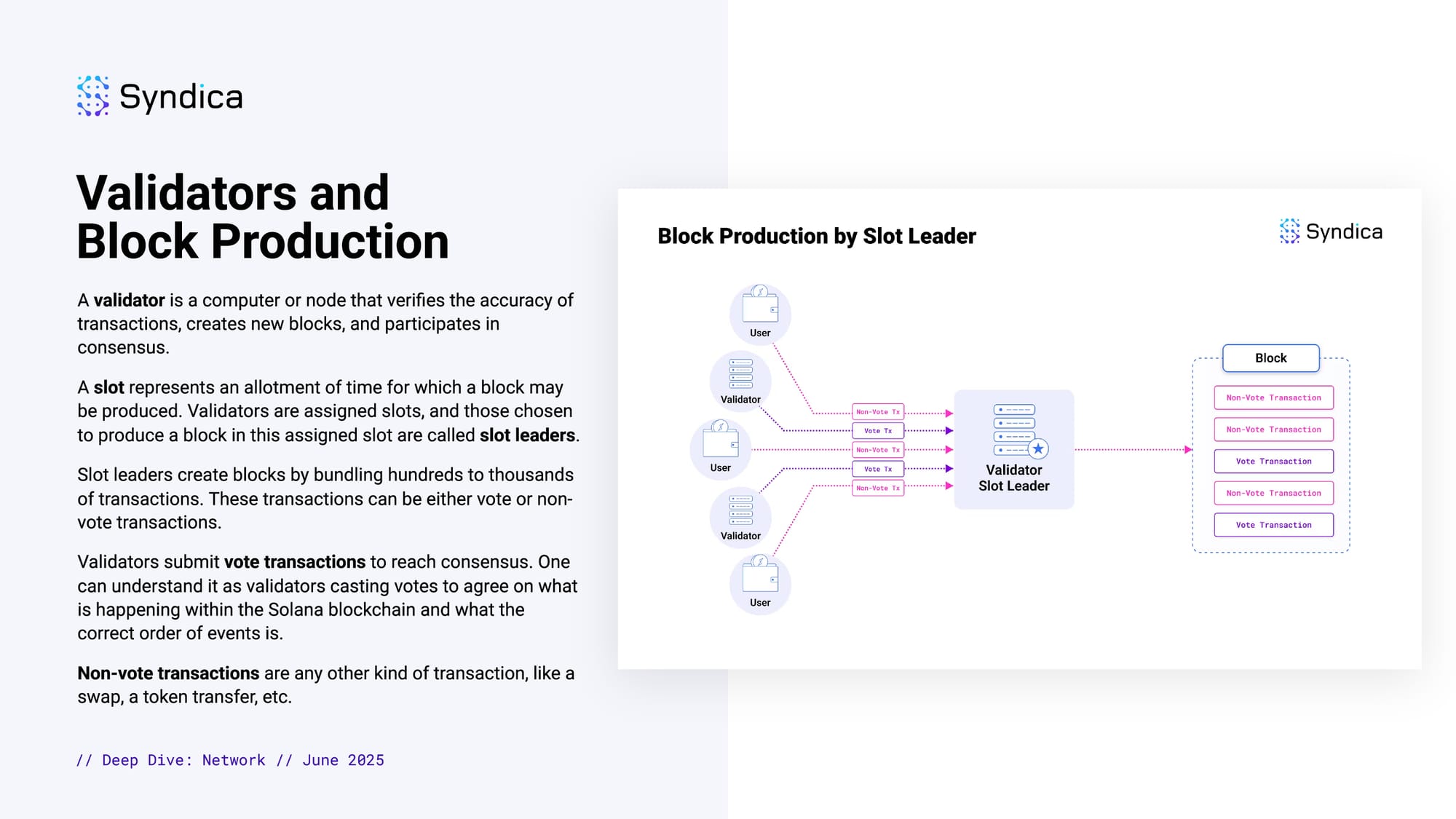
Validators and Block Production
A validator is a computer or node that verifies the accuracy of transactions, creates new blocks, and participates in consensus.
A slot represents an allotment of time for which a block may be produced. Validators are assigned slots, and those chosen to produce a block in this assigned slot are called slot leaders.
Slot leaders create blocks by bundling hundreds to thousands of transactions. These transactions can be either vote or non-vote transactions.
Validators submit vote transactions to reach consensus. One can understand it as validators casting votes to agree on what is happening within the Solana blockchain and what the correct order of events is.
Non-vote transactions are any other kind of transaction, like a swap, a token transfer, etc.
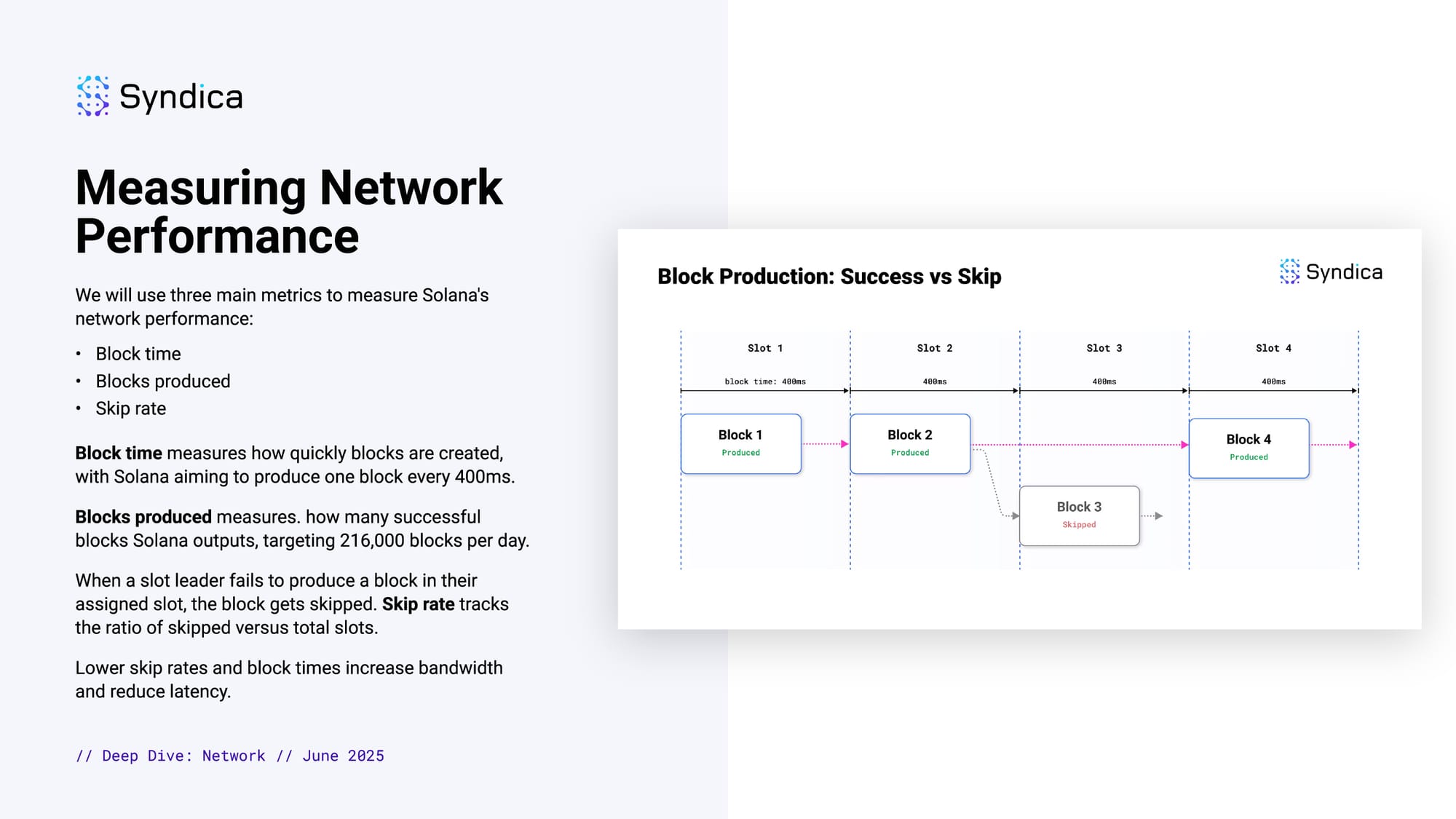
Measuring Network Performance
We will use three main metrics to measure Solana's network performance:
- Block time
- Blocks produced
- Skip rate
Block time measures how quickly blocks are created, with Solana aiming to produce one block every 400ms.
Blocks produced measures. how many successful blocks Solana outputs, targeting 216,000 blocks per day.
When a slot leader fails to produce a block in their assigned slot, the block gets skipped. Skip rate tracks the ratio of skipped versus total slots.
Lower skip rates and block times increase bandwidth and reduce latency.
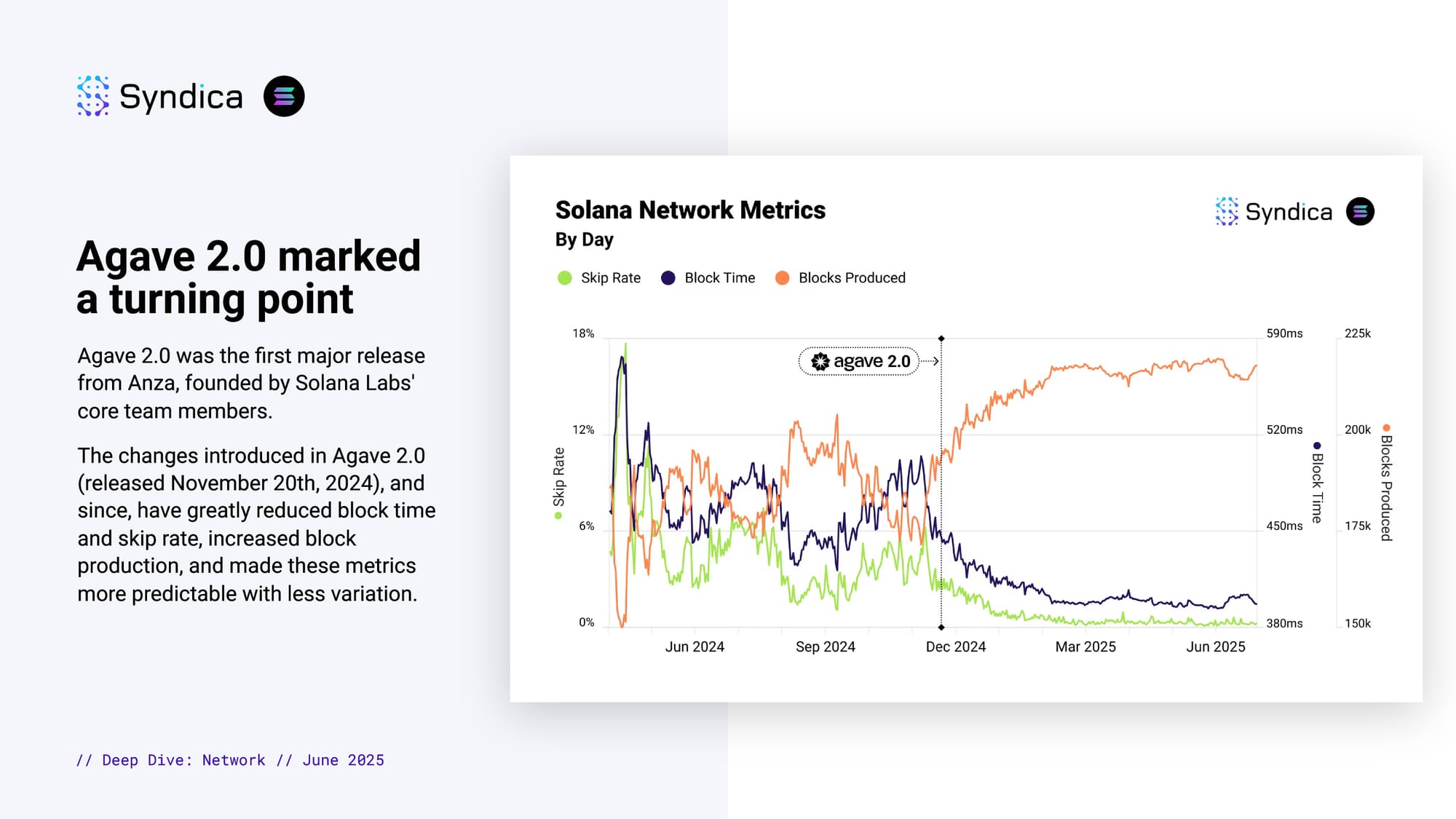
Agave 2.0 marked a turning point
Agave 2.0 was the first major release from Anza, founded by Solana Labs' core team members.
The changes introduced in Agave 2.0 (released November 20th, 2024), and since, have greatly reduced block time and skip rate, increased block production, and made these metrics more predictable with less variation.
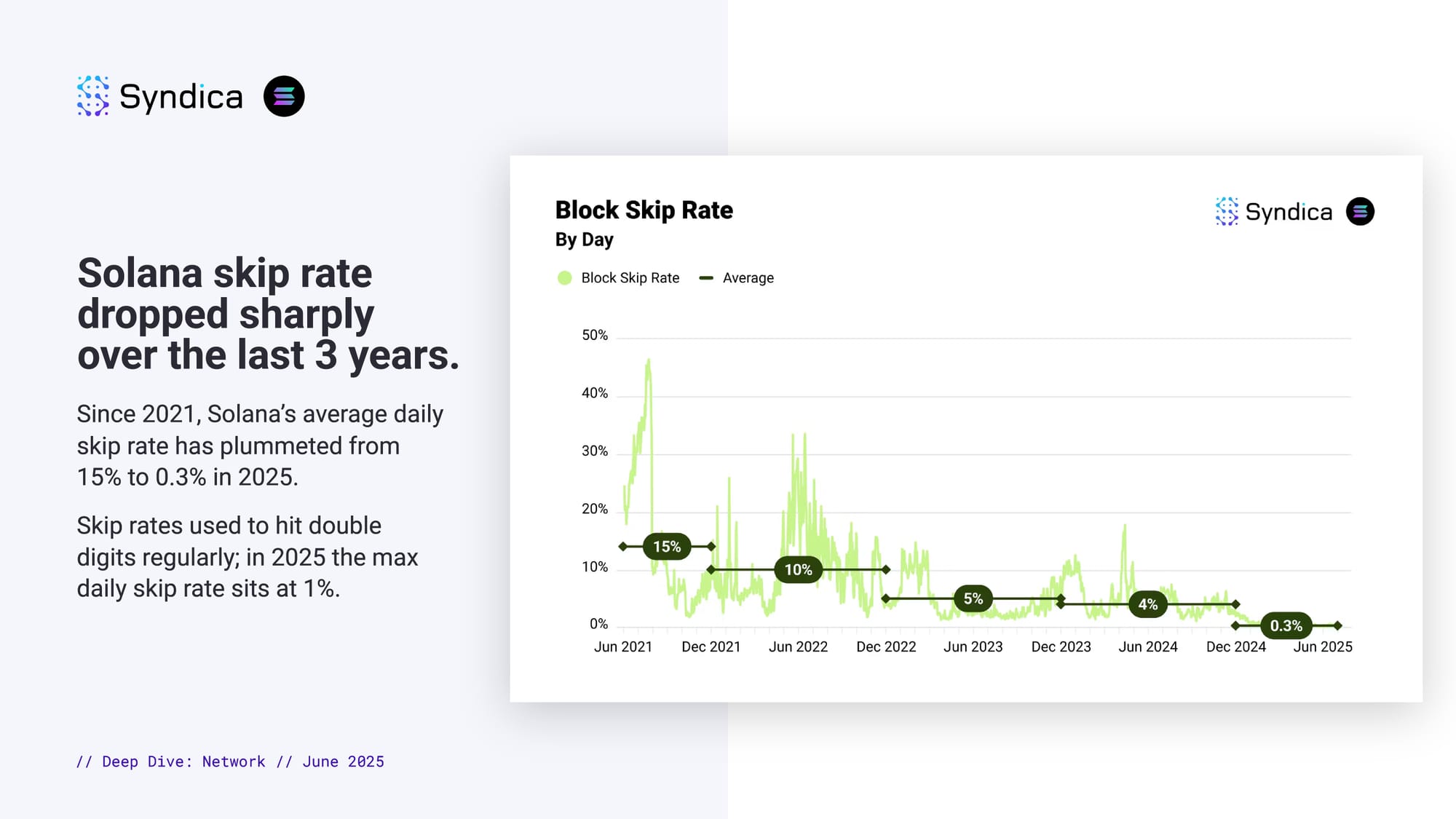
Solana skip rate dropped sharply over the last 3 years.
Since 2021, Solana’s average daily skip rate has plummeted from 15% to 0.3% in 2025.
Skip rates used to hit double digits regularly; in 2025 the max daily skip rate sits at 1%.
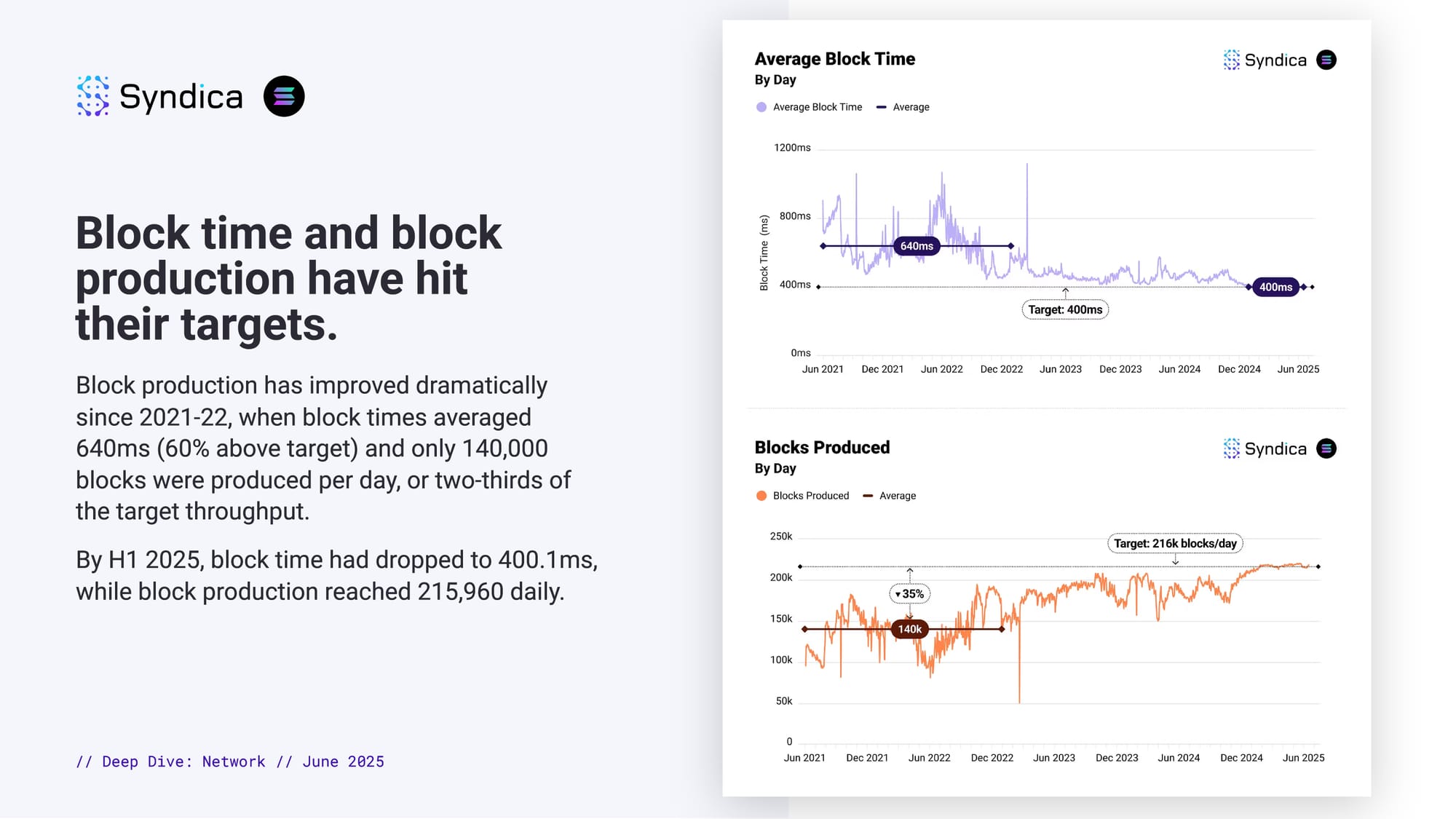
Block time and block production have hit their targets.
Block production has improved dramatically since 2021-22, when block times averaged 640ms (60% above target) and only 140,000 blocks were produced per day, or two-thirds of the target throughput.
By H1 2025, block time had dropped to 400.1ms, while block production reached 215,960 daily.
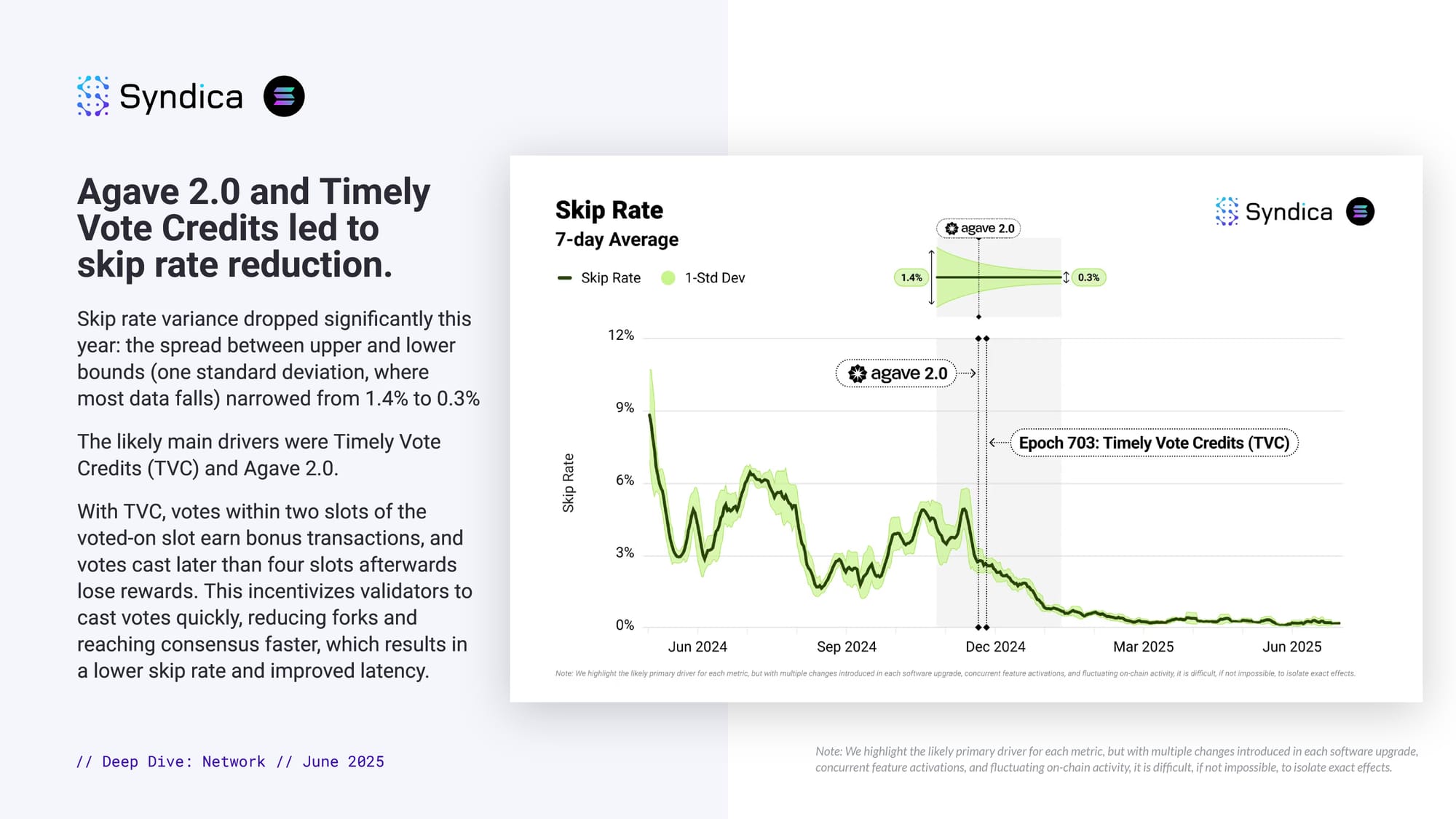
Agave 2.0 and Timely Vote Credits led to skip rate reduction.
Skip rate variance dropped significantly this year: the spread between upper and lower bounds (one standard deviation, where most data falls) narrowed from 1.4% to 0.3%
The likely main drivers were Timely Vote Credits (TVC) and Agave 2.0.
With TVC, votes within two slots of the voted-on slot earn bonus transactions, and votes cast later than four slots afterwards lose rewards. This incentivizes validators to cast votes quickly, reducing forks and reaching consensus faster, which results in a lower skip rate and improved latency.
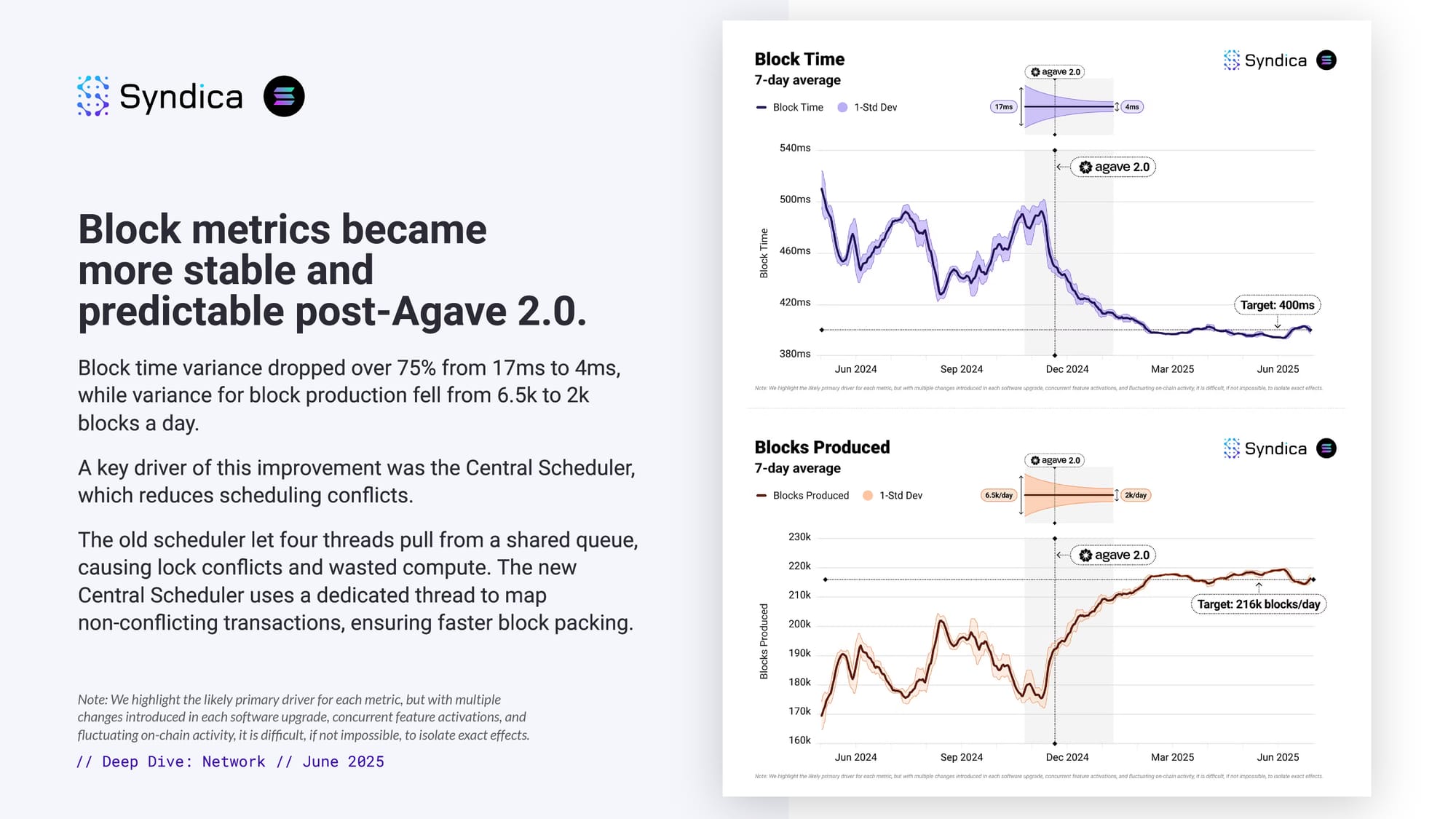
Block metrics became more stable and predictable post-Agave 2.0.
Block time variance dropped over 75% from 17ms to 4ms, while variance for block production fell from 6.5k to 2k blocks a day.
A key driver of this improvement was the Central Scheduler, which reduces scheduling conflicts.
The old scheduler let four threads pull from a shared queue, causing lock conflicts and wasted compute. The new Central Scheduler uses a dedicated thread to map
non-conflicting transactions, ensuring faster block packing.
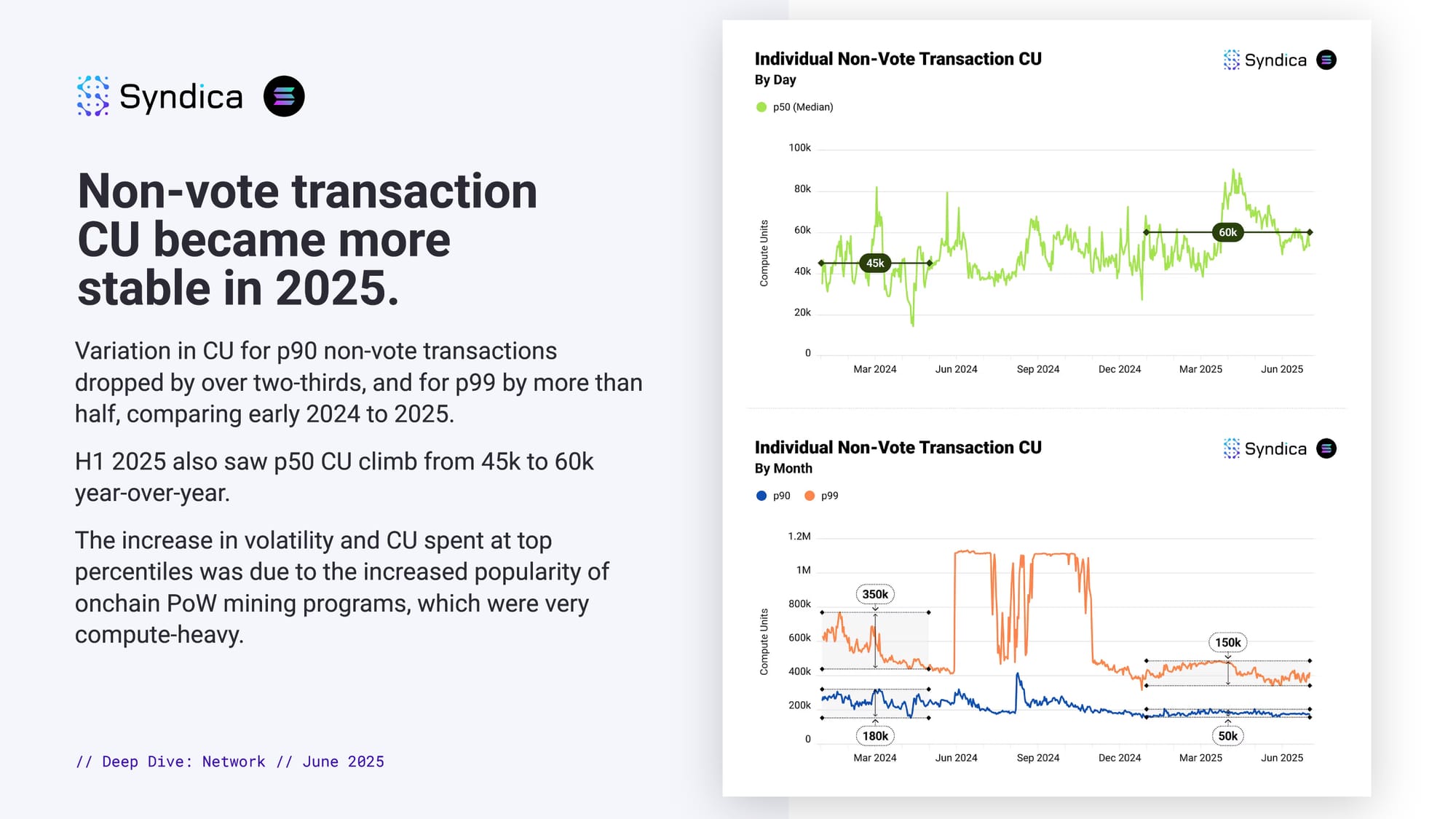
Non-vote transaction CU became more stable in 2025.
Variation in CU for p90 non-vote transactions dropped by over two-thirds, and for p99 by more than half, comparing early 2024 to 2025.
H1 2025 also saw p50 CU climb from 45k to 60k year-over-year.
The increase in volatility and CU spent at top percentiles was due to the increased popularity of onchain PoW mining programs, which were very compute-heavy.
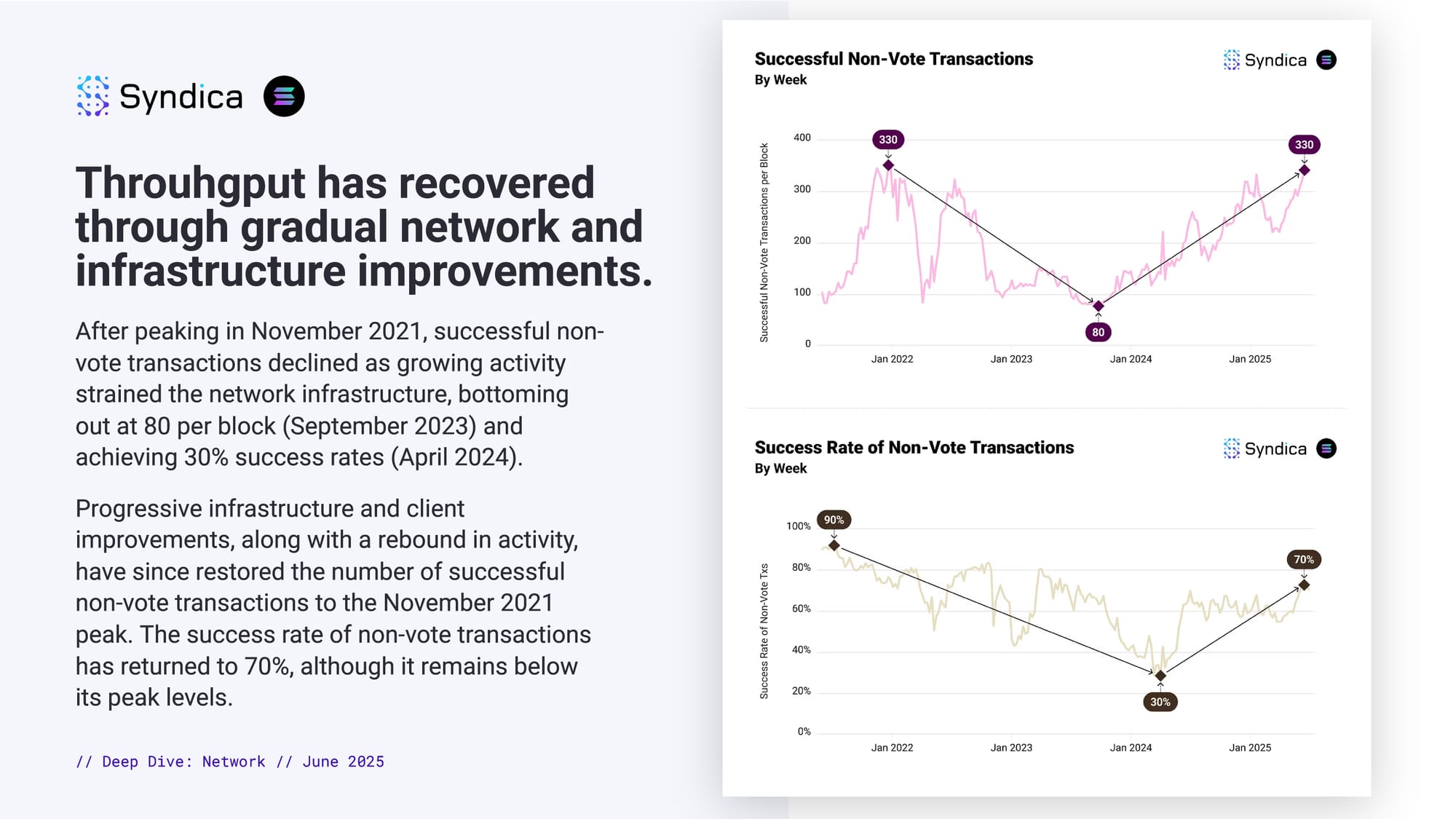
Throuhgput has recovered through gradual network and infrastructure improvements.
After peaking in November 2021, successful non-vote transactions declined as growing activity strained the network infrastructure, bottoming out at 80 per block (September 2023) and achieving 30% success rates (April 2024).
Progressive infrastructure and client improvements, along with a rebound in activity, have since restored the number of successful non-vote transactions to the November 2021 peak. The success rate of non-vote transactions has returned to 70%, although it remains below its peak levels.
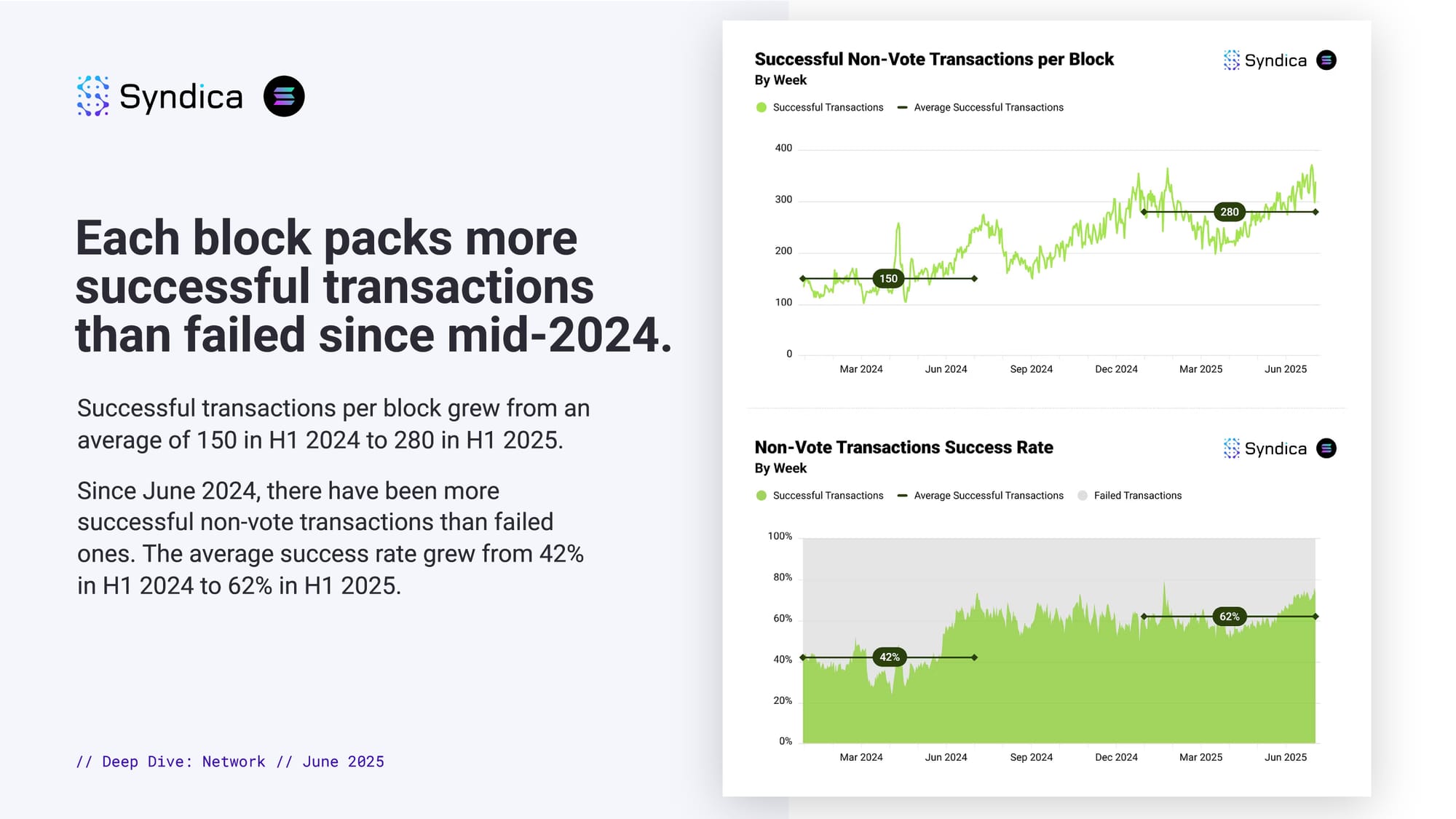
Each block packs more successful transactions than failed since mid-2024.
Successful transactions per block grew from an average of 150 in H1 2024 to 280 in H1 2025.
Since June 2024, there have been more successful non-vote transactions than failed ones. The average success rate grew from 42% in H1 2024 to 62% in H1 2025.
Part II - Validator Clients
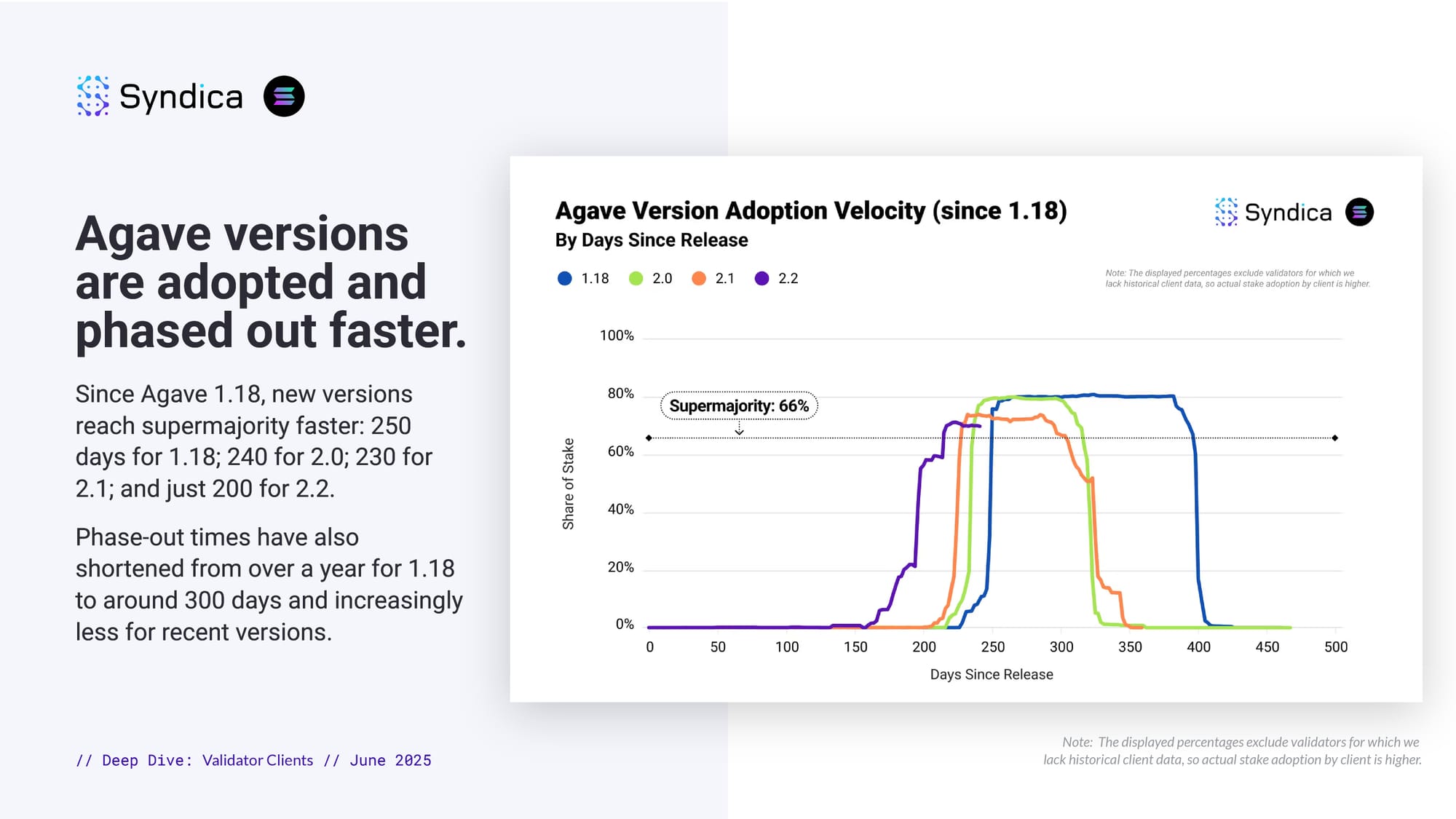
Agave versions are adopted and phased out faster.
Since Agave 1.18, new versions reach supermajority faster: 250 days for 1.18; 240 for 2.0; 230 for 2.1; and just 200 for 2.2.
Phase-out times have also shortened from over a year for 1.18 to around 300 days and increasingly less for recent versions.
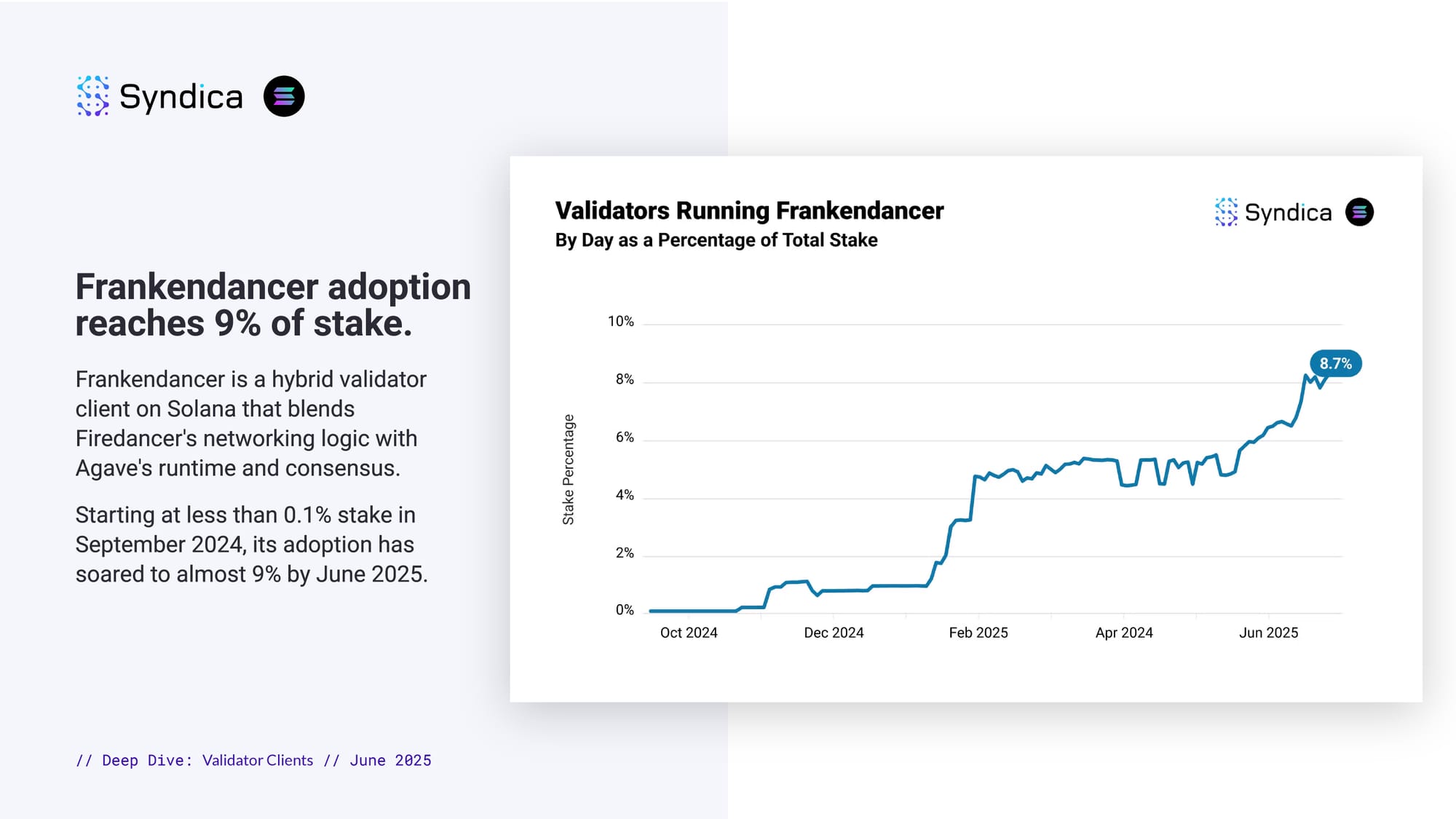
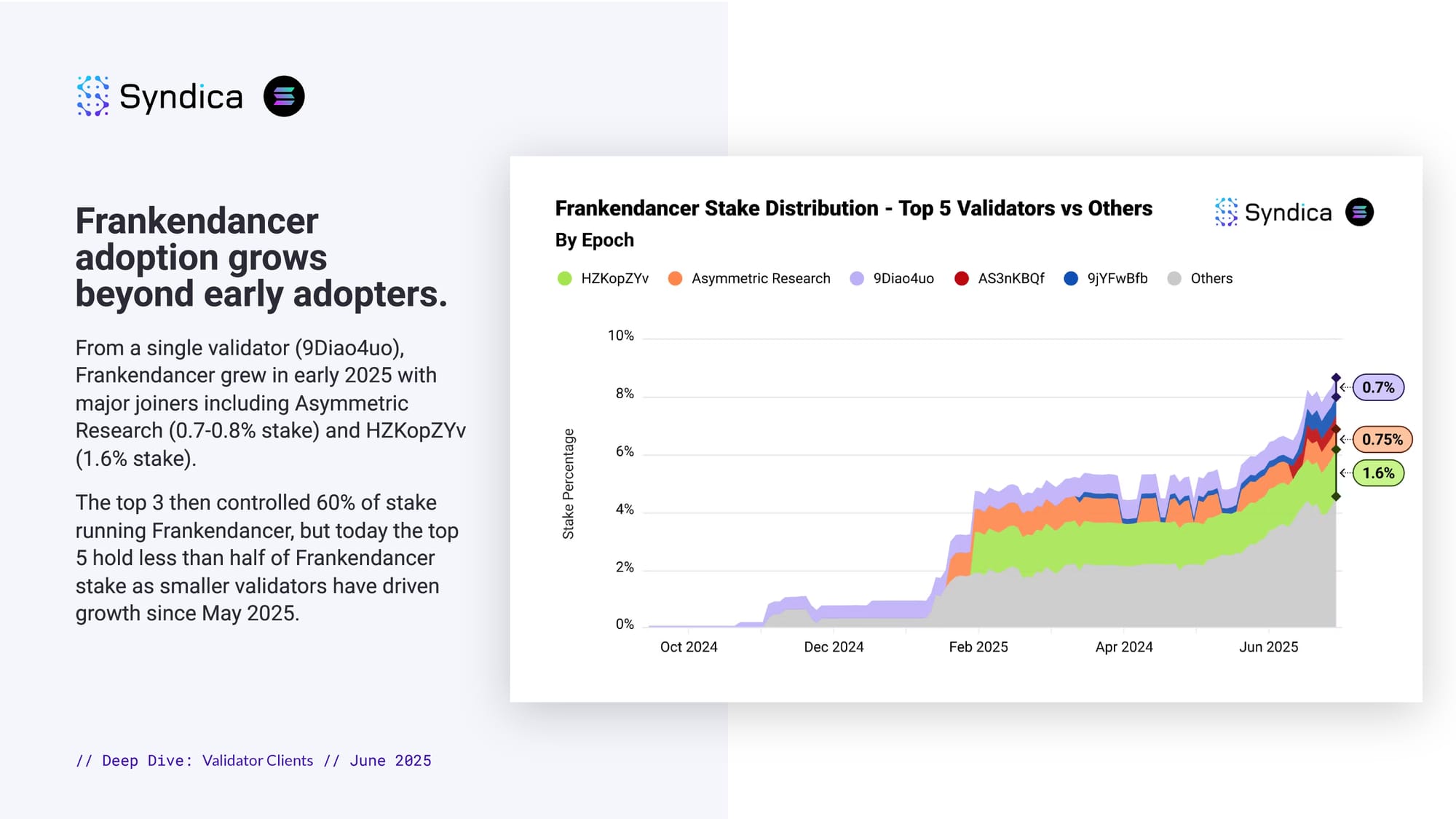
Frankendancer adoption grows beyond early adopters.
From a single validator (9Diao4uo), Frankendancer grew in early 2025 with major joiners including Asymmetric Research (0.7-0.8% stake) and HZKopZYv (1.6% stake).
The top 3 then controlled 60% of stake running Frankendancer, but today the top 5 hold less than half of Frankendancer stake as smaller validators have driven growth since May 2025.
Part III - Programs
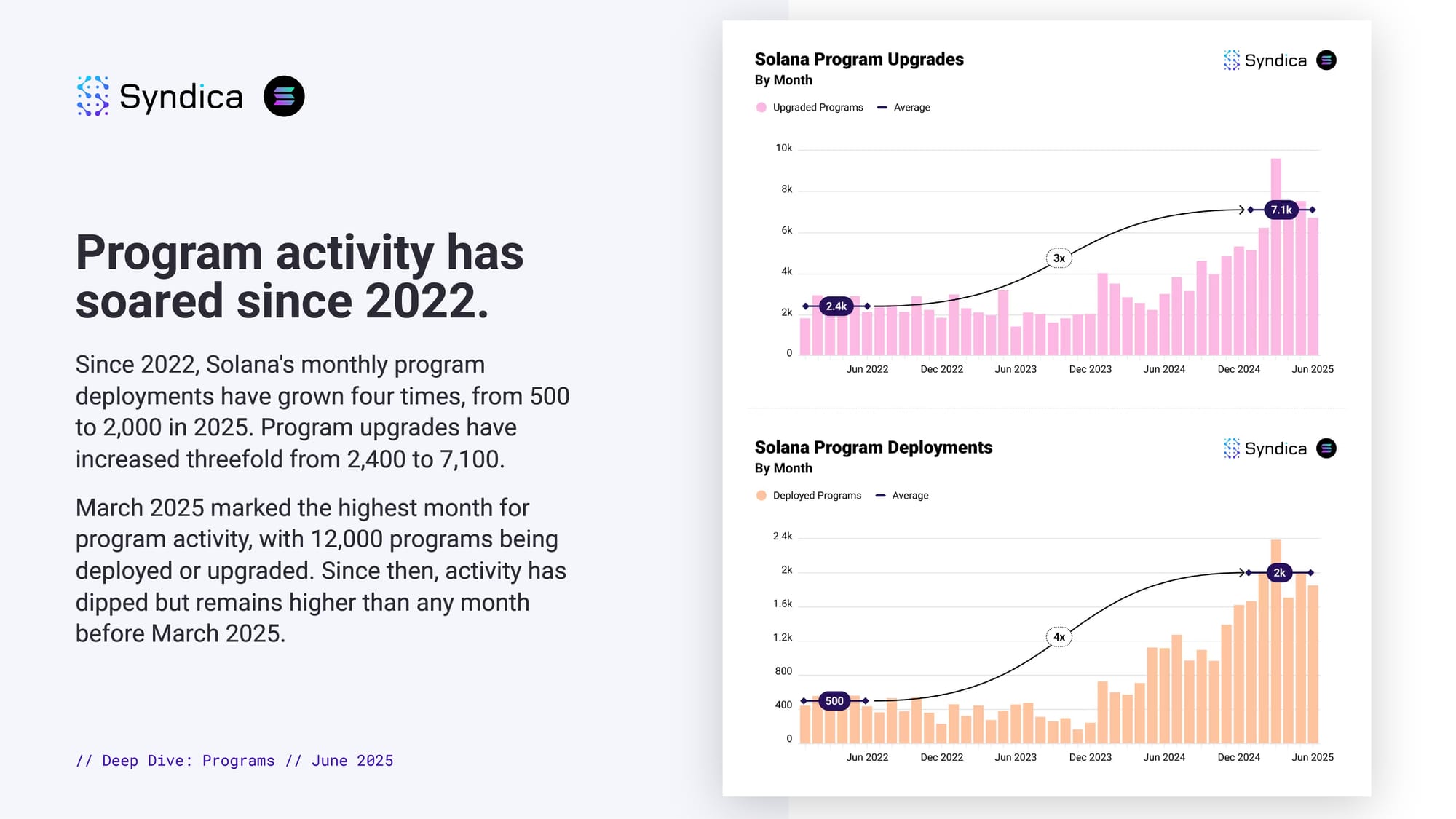
Program activity has soared since 2022.
Since 2022, Solana's monthly program deployments have grown four times, from 500 to 2,000 in 2025. Program upgrades have increased threefold from 2,400 to 7,100.
March 2025 marked the highest month for program activity, with 12,000 programs being deployed or upgraded. Since then, activity has dipped but remains higher than any month before March 2025.
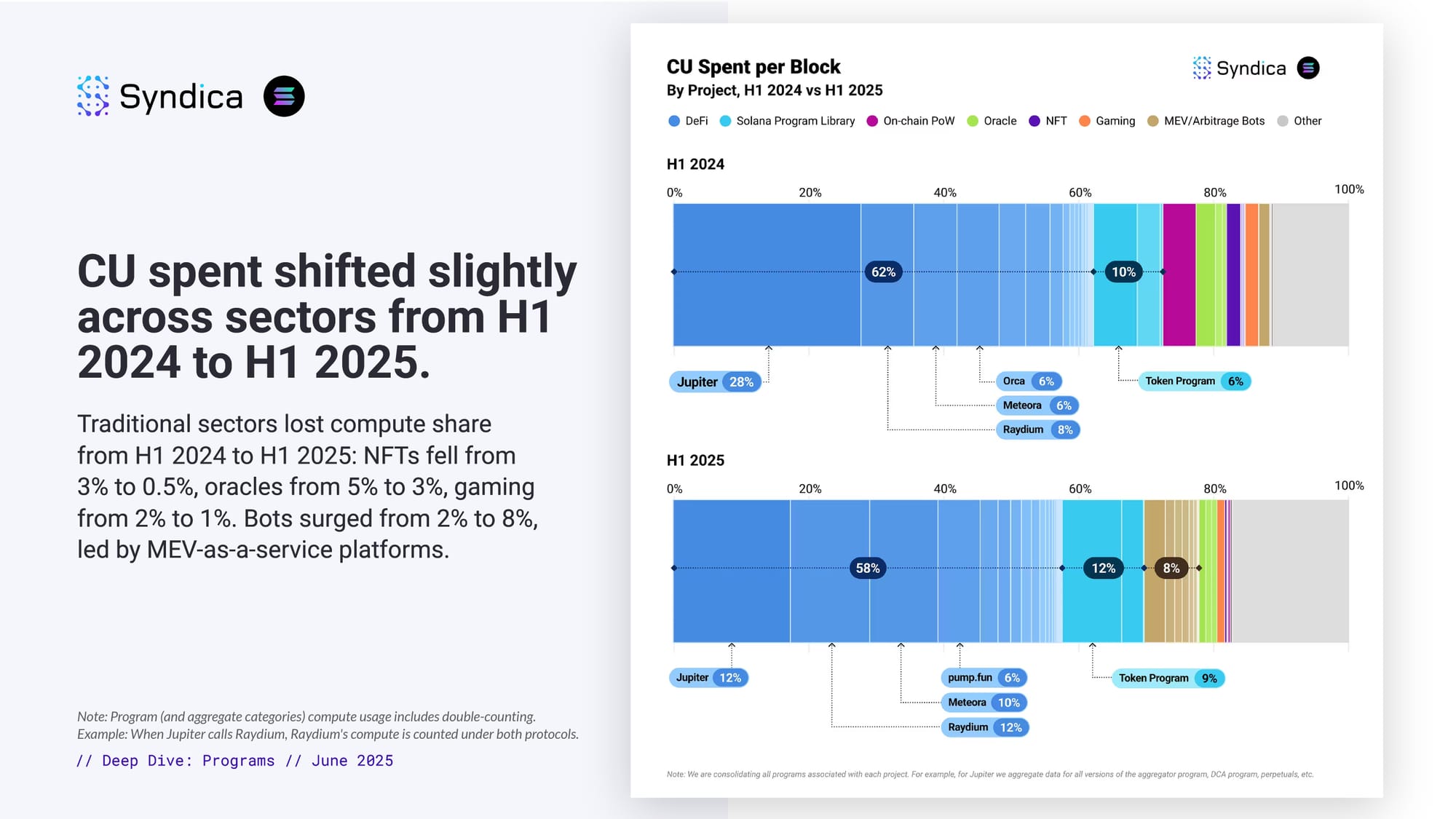
CU spent shifted slightly across sectors from H1 2024 to H1 2025.
Traditional sectors lost compute share from H1 2024 to H1 2025: NFTs fell from 3% to 0.5%, oracles from 5% to 3%, gaming from 2% to 1%. Bots surged from 2% to 8%, led by MEV-as-a-service platforms.
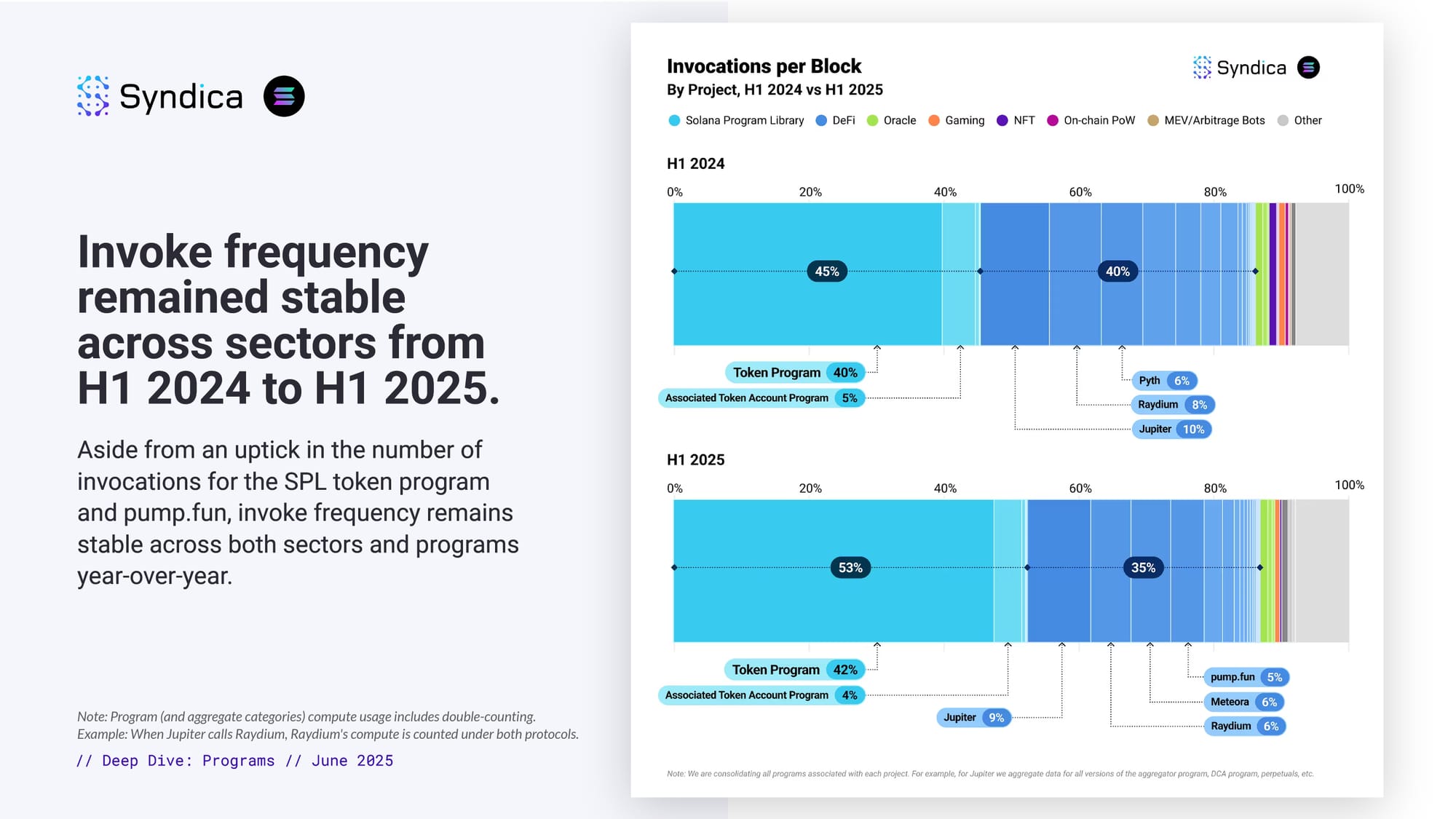
Invoke frequency remained stable across sectors from H1 2024 to H1 2025.
Aside from an uptick in the number of invocations for the SPL token program and pump.fun, invoke frequency remains stable across both sectors and programs year-over-year.



